Are you ready to take the leap into homeownership? Securing the best mortgage rate possible can save you thousands of dollars over the life of your loan. But with countless lenders, fluctuating rates, and seemingly endless options, how do you ensure you’re getting the most favorable terms? Our comprehensive guide to tips for getting the best mortgage rate is here to help! Learn how to navigate the competitive market, boost your creditworthiness, and negotiate with lenders like a pro, all while unlocking the true potential of your dream home. Say goodbye to mortgage stress and hello to long-term savings!
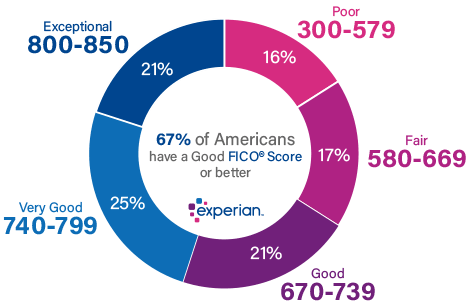
Improve your credit score: A higher credit score is a strong indicator of your financial responsibility, making you a more attractive candidate for a favorable mortgage rate

Boosting your credit score is a crucial aspect of securing the best mortgage rate. Lenders view a higher credit score as proof of your financial reliability, increasing your chances of obtaining a competitive mortgage rate. To improve your credit score, start by reviewing your credit report for inaccuracies and disputing any errors. Focus on timely bill payments, reducing your debt-to-income ratio, and maintaining a low credit utilization rate. Additionally, avoid opening new credit lines or making large purchases prior to applying for a mortgage, as these actions can temporarily lower your credit score. By consistently demonstrating responsible financial behavior, you’ll enhance your creditworthiness and position yourself for an exceptional mortgage rate.
To improve your credit score, make timely payments on your debts, maintain low credit card balances, and avoid taking on new debt.

One of the most crucial factors in securing the best mortgage rate is maintaining a healthy credit score. To achieve this, it’s essential to be diligent in making timely payments on all your debts, including loans, credit cards, and utility bills. Keeping your credit card balances low demonstrates responsible credit management and reduces your credit utilization ratio, which positively impacts your credit score. Additionally, refrain from taking on new debt or applying for multiple credit lines, as this can lead to hard inquiries on your credit report, resulting in a temporary dip in your credit score. By focusing on these credit-building strategies, you’ll be well on your way to securing an attractive mortgage rate for your dream home.
Save for a larger down payment: A larger down payment not only reduces the amount you need to borrow but also demonstrates to lenders that you are financially prepared for homeownership
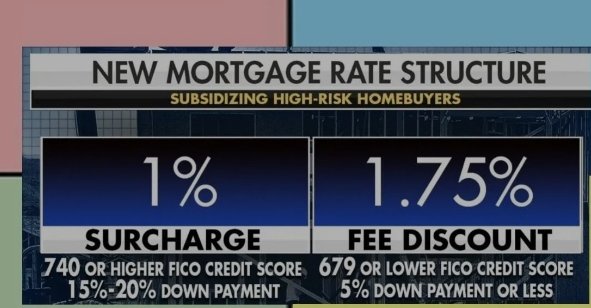
One of the most effective strategies for securing the best mortgage rate is to save for a larger down payment. By putting down a more substantial sum, you’ll not only decrease the amount you need to borrow, but also showcase your financial readiness for homeownership. Lenders are likely to offer more competitive rates to borrowers who present lower risk, and a larger down payment is a strong indicator of financial stability. Moreover, reaching the 20% down payment milestone can help you avoid costly private mortgage insurance (PMI) premiums, further reducing your overall loan expenses. Therefore, taking the time to diligently save for a bigger down payment is a smart move when aiming for the best mortgage rate.
A down payment of 20% or more can help you secure a better mortgage rate, as it lowers the lender’s risk.
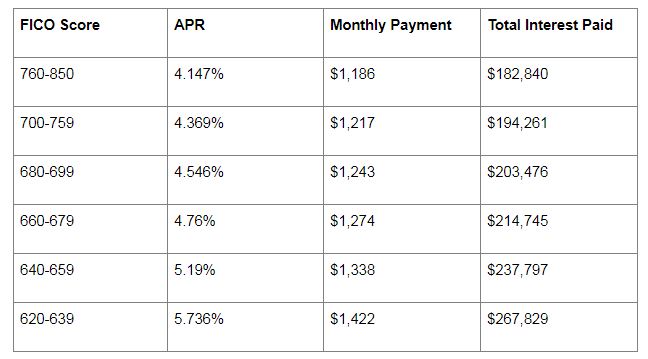
A substantial down payment of 20% or more not only demonstrates your financial commitment but also significantly reduces the lender’s risk, making them more likely to offer you a competitive mortgage rate. By investing a larger amount upfront, you establish a strong foundation for your mortgage and decrease the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio, which lenders view favorably. Furthermore, a lower LTV ratio helps you avoid the additional cost of private mortgage insurance (PMI), ultimately saving you money in the long run. Therefore, diligently saving for a sizeable down payment is a crucial strategy for securing the best mortgage rate and minimizing your overall borrowing costs.
Shop around and compare rates: Don’t settle for the first mortgage offer you receive; instead, shop around and compare rates from multiple lenders.

When embarking on the journey to secure the ideal mortgage rate, it’s crucial not to limit your options by accepting the first offer that comes your way. By shopping around and comparing rates from various lenders, you significantly increase your chances of finding a favorable deal. This process involves researching and obtaining quotes from multiple financial institutions, such as banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Carefully evaluate each proposal to identify the most competitive interest rates, terms, and fees. Remember, even a slight difference in the mortgage rate can result in substantial savings over the life of the loan. By being proactive and diligent in your search, you can confidently secure the best mortgage rate tailored to your financial needs.