If you’re a student looking to purchase a home, understanding the difference between a government-insured mortgage and a conventional mortgage is key. Whether you’re 18 or older, it pays to be knowledgeable about the different types of mortgages available and the potential benefits of each. In this article, I’ll break down the differences between government-insured mortgages and conventional mortgages, so you can make an informed decision.
Research government-insured mortgages.
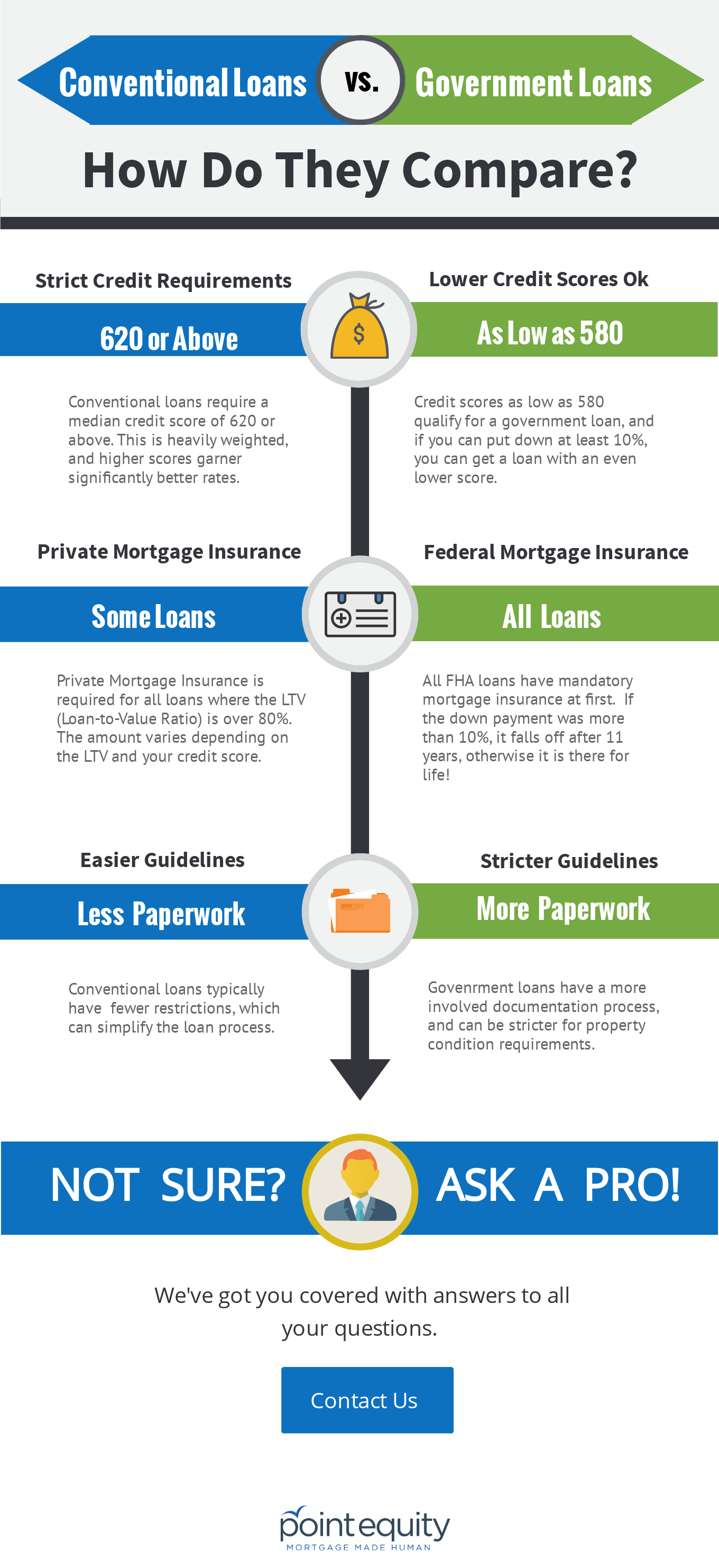
Researching government-insured mortgages can be confusing. The best way to start is to compare them to conventional mortgages. Government-insured mortgages usually have lower interest rates, but require a higher down payment. They also have more restrictions on the loan amount and the borrower’s credit score. Knowing the differences between the two types of mortgages can help you make the best decision for your financial needs.
Compare to conventional mortgages.

Comparing a government-insured mortgage to a conventional loan, the main difference is that the government insures the loan. This means that if you default on your payments, the government will cover the lender’s losses. This makes government-insured mortgages safer than conventional loans, since they come with a lower risk of default. However, they often come with higher interest rates and stricter eligibility requirements.
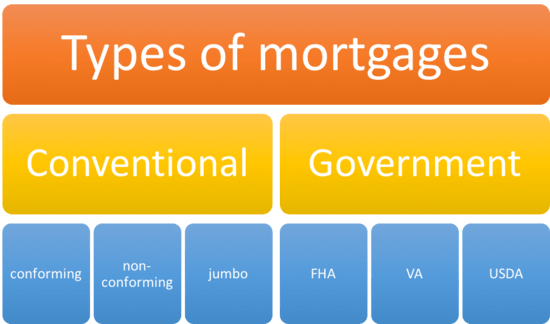
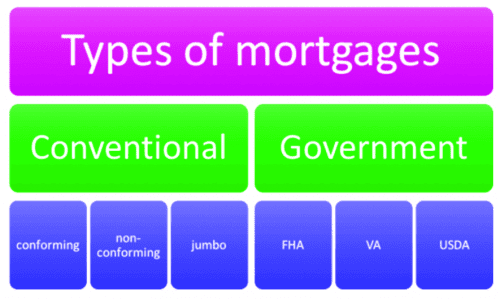
Identify government insurance requirements.

If you want to know the difference between a government-insured and a conventional mortgage, you should first identify the government insurance requirements. Government-insured mortgages are backed by agencies such as FHA, VA, and USDA, making them more attractive to buyers since they may require smaller down payments and offer flexible credit criteria. Conventional mortgages, on the other hand, don’t have any government insurance and require larger down payments and stricter credit requirements.
Identify conventional loan requirements.

Conventional loans are not insured by the government and usually require a higher credit score and larger down payment than government-insured loans. When applying for a conventional loan, lenders typically require a minimum credit score of 620, proof of income and assets, and a debt-to-income ratio of no more than 50%. The down payment amount can range from 3-20%, depending on the type of loan you’re getting.
Consider pros and cons of each.
When considering a government-insured mortgage vs. a conventional mortgage, it’s important to look at the pros and cons of each. Government-insured mortgages tend to have lower interest rates and can be easier to qualify for, although they may come with higher fees. Conventional mortgages typically don’t require additional fees and can offer more flexibility in terms of repayment plans, but may require higher credit scores. Ultimately, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each based on your individual needs.
Choose the best option.
Choosing between a government-insured and conventional mortgage can be confusing. But, if you take the time to understand the differences between the two, it will be easier to select the best option for you. Government-insured mortgages are backed by the federal government, so they often offer easier qualification requirements, lower interest rates, and more flexible payment options. Conventional mortgages are not backed by the government, but may offer higher loan amounts and better terms in some cases. Understanding the differences between the two can help you make an educated decision about which mortgage type is right for you.